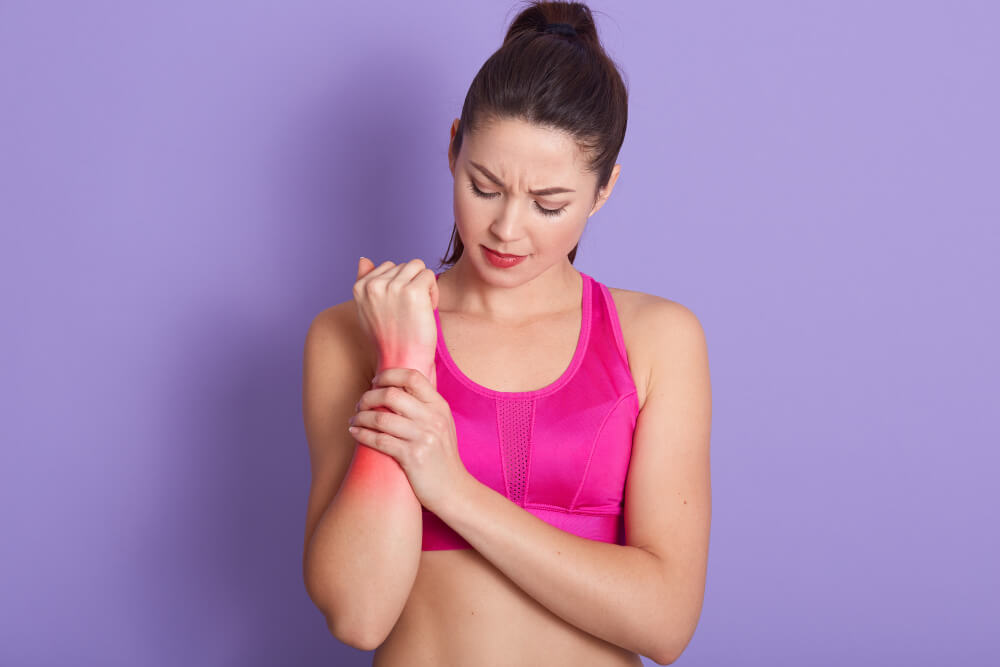
Wrist Pain Woes? Find Relief with an Orthopedic Specialist
Wrist pain is a common complaint that can arise from a variety of causes, ranging from minor sprains to more serious conditions. While many cases resolve with self-care measures like rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers, persistent or severe wrist pain warrants a visit to an orthopedic specialist. Orthopedic surgeons are medical professionals specializing in conditions of the musculoskeletal system, including the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. They are equipped to diagnose the underlying cause of your wrist pain and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Common Causes of Wrist Pain
Overuse Injuries
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Repetitive motions, such as typing or using a mouse, can compress the median nerve in the wrist, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons in the wrist, often caused by repetitive activities, can result in pain and stiffness.
Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint disease can affect the wrist, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease that can affect the joints, including the wrist, leading to inflammation and pain.
Fractures and Dislocations
Traumatic injuries can cause fractures or dislocations of the wrist bones, resulting in severe pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the wrist.
Other Conditions
- Ganglion Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can form on the back of the wrist, causing pain and discomfort.
- Trigger Finger: A condition where a finger gets stuck in a bent position and may snap straight when forced.
- Referred Pain: Wrist pain can sometimes be caused by conditions in other parts of the body, such as the neck or shoulder.
When to See an Orthopedic Specialist
While many cases of wrist pain can be managed with self-care, it’s essential to consult an orthopedic specialist if:
- Wrist pain persists despite home treatment for several weeks.
- Pain is severe, debilitating, or interferes with daily activities.
- You experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in your hand or fingers.
- There is visible swelling, deformity, or bruising around the wrist.
- You have a history of wrist injuries or medical conditions.
Diagnosis of Wrist Pain
An orthopedic specialist will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause of your wrist pain. This may involve:
- Medical History: Discussing your symptoms, past injuries, and overall health.
- Physical Examination: Assessing the wrist for tenderness, swelling, range of motion, and neurological function.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be ordered to visualize the bones, soft tissues, and nerves in the wrist.
Treatment Options for Wrist Pain
Treatment for wrist pain depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Orthopedic specialists offer a range of treatment options, including:
Non-surgical Treatments
- Rest and Immobilization: Avoiding activities that aggravate the wrist and using a splint or brace can help reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve wrist strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the wrist joint.
Surgical Interventions
- Carpal Tunnel Release: For carpal tunnel syndrome, surgery involves releasing the ligament compressing the median nerve.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that allows the surgeon to visualize and repair damaged tissues within the wrist joint.
- Fusion: In severe cases of arthritis, fusing the wrist bones together can provide stability and pain relief.
Preventing Wrist Pain
To prevent wrist pain and injuries, consider the following tips:
- Maintain good posture while using computers or performing repetitive tasks.
- Take breaks from activities that strain the wrist.
- Strengthen the muscles in your hands and wrists through exercises.
- Use ergonomic keyboards and mice.
- Wear wrist splints or braces for support.
By understanding the potential causes of wrist pain and seeking appropriate care, you can effectively manage your symptoms and regain full use of your hand.

