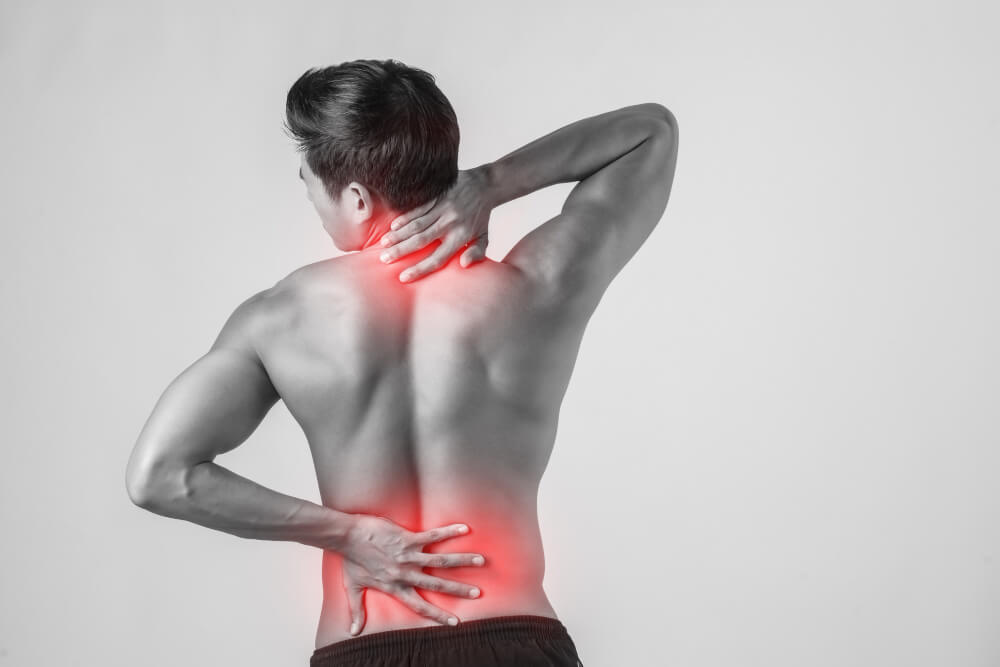
Musculoskeletal Problems: A Comprehensive Guide to Orthopedic Care
Musculoskeletal problems are common and can affect people of all ages. They can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, limiting mobility and affecting overall well-being. Orthopedic surgeons are medical specialists who focus on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions affecting the bones, muscles, joints, and ligaments.
Common Musculoskeletal Conditions
Musculoskeletal problems can vary widely, but some of the most common conditions include:
- Arthritis Degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Fractures Broken bones, including simple fractures, compound fractures, and stress fractures.
- Sprains and Strains Overstretching or tearing of muscles or ligaments.
- Tendinitis and Bursitis Inflammation of tendons or bursae, often caused by overuse.
- Back Pain Chronic or acute pain in the back, often caused by herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or muscle strain.
- Joint Pain Pain in the joints, such as the knees, shoulders, or hips.
- Sports Injuries Injuries related to athletic activities, including sprains, strains, and fractures.
The Role of Orthopedic Doctor
Orthopedic surgeons play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal problems:
- Diagnosis Conducting thorough physical examinations, reviewing medical history, and ordering imaging tests.
- Treatment Planning Developing personalized treatment plans based on the specific condition and patient needs.
- Non-Surgical Treatment Offering non-surgical options such as physical therapy, medications, and injections.
- Surgical Treatment Performing surgical procedures when necessary, including joint replacement, arthroscopy, and fracture repair.
- Rehabilitation Overseeing rehabilitation programs to help patients recover and regain function.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Musculoskeletal Problems
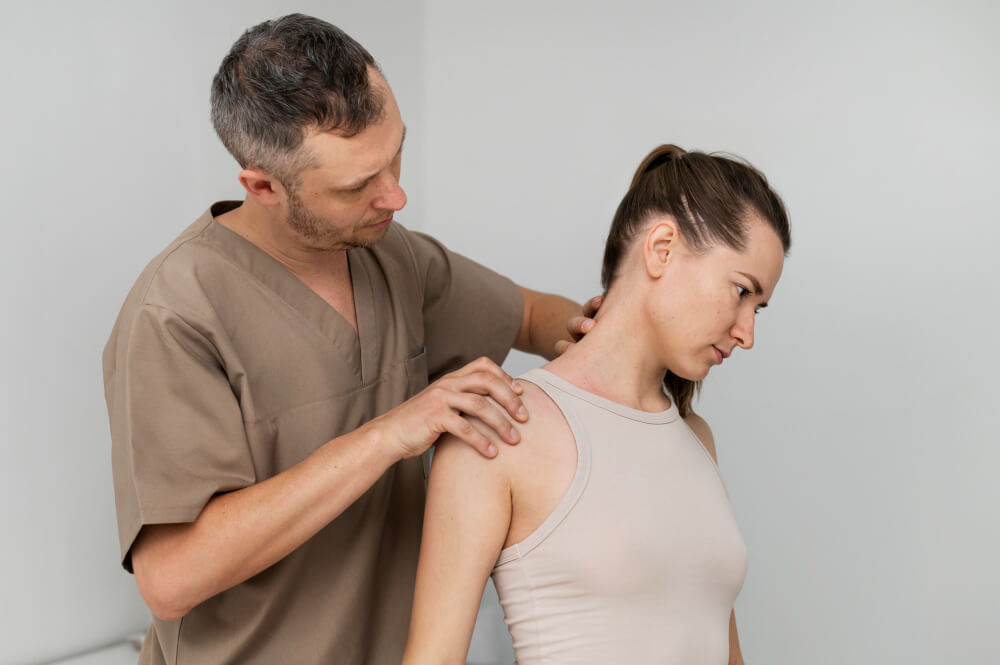
Many musculoskeletal problems can be treated without surgery:
- Physical Therapy Exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Medications Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, or corticosteroids.
- Braces or Splints Immobilizing injured body parts to promote healing.
- Lifestyle Modifications Adjusting activities or habits to reduce stress on the affected area.
Surgical Treatment for Musculoskeletal Problems
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat musculoskeletal conditions:
- Joint Replacement Replacing damaged joints with artificial implants.
- Arthroscopy Minimally invasive surgery using a small camera and surgical instruments.
- Fracture Repair Repairing broken bones using pins, screws, or plates.
- Tendon Repair Repairing torn or damaged tendons.
- Spinal Surgery Treating conditions such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation is an essential part of recovering from musculoskeletal injuries or surgeries:
- Physical Therapy Exercises to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Occupational Therapy Activities to improve daily living skills and function.
- Gradual Return to Activity Slowly increasing activity levels to prevent reinjury.
Preventing Musculoskeletal Problems
Adopting preventive measures can help reduce the risk of musculoskeletal problems:
- Proper Posture Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting.
- Regular Exercise Strengthening muscles and improving flexibility.
- Healthy Weight Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Proper Ergonomics Creating a comfortable and supportive work environment.
- Adequate Rest and Recovery Allowing sufficient time for rest and recovery.
Seeking expert care from an orthopedic surgeon is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal problems. By following a personalized treatment plan and incorporating preventive measures, individuals can improve their quality of life and regain optimal function.